Graphs
Intro
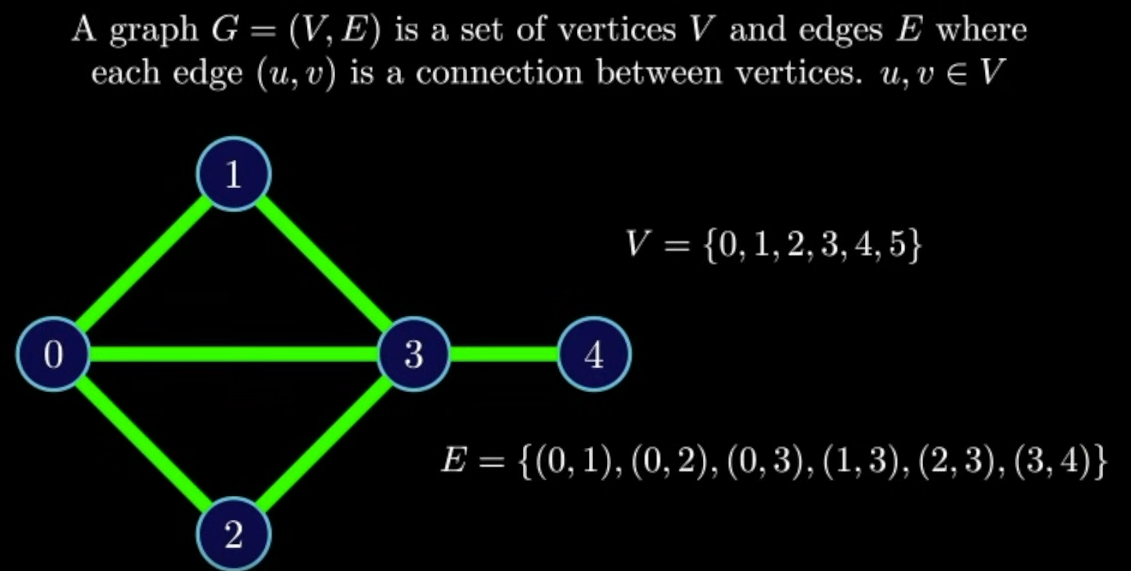
- Network that helps define and visualize relationships between various components
- Layout of the graph is not part of the graph. Following two are the same graph
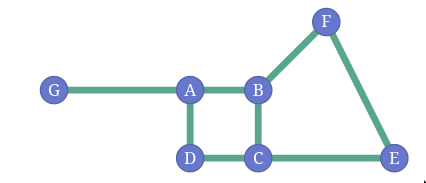
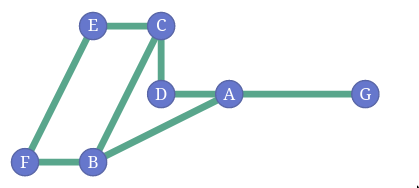
- You can define different networks in the same data. Some networks are more useful than others.
- Possible use
- Can be used in infinite ways. If you can make your data look like a graph, you can reuse a wide variety of graph algorithms.
- Eg. You could represent your game’s economy as a graph, with wheat and bread as nodes and baking as an edge.
- Introduction to Behavior Trees | Game tree | State Game Programming | Polygonal Map Generation
- Graphs and networks | plus.maths.org
Basic terms
Path: Sequence ofverticesconnected byedgesConnectivityVerted:Connected:2verticesareconnectedis there’s apathconnecting themGraph:Connected: When every node has a path to another nodeConnected Component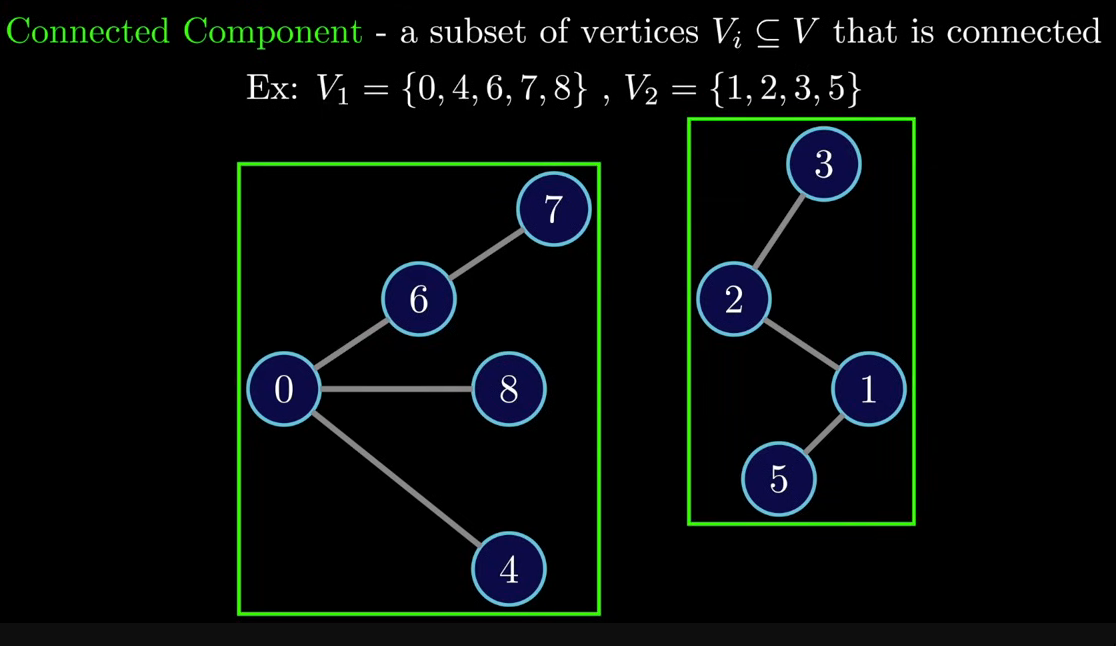
Common problems
- Does a path exist
- Is the graph connected
- What’s the shortest path
- Does it contain cycle
- Given a set of k colors, can we assign colors to each vertex so that no two neighbors are assigned the same color? (Sudoku problem)
- Does a path exist that uses every
edgeexactly once? - Does a path exist that uses every
vertexexactly once? (NP Hard, See Complexity Theory ) - Solving the minimum cut problem for undirected graphs | Hacker News
Flavors
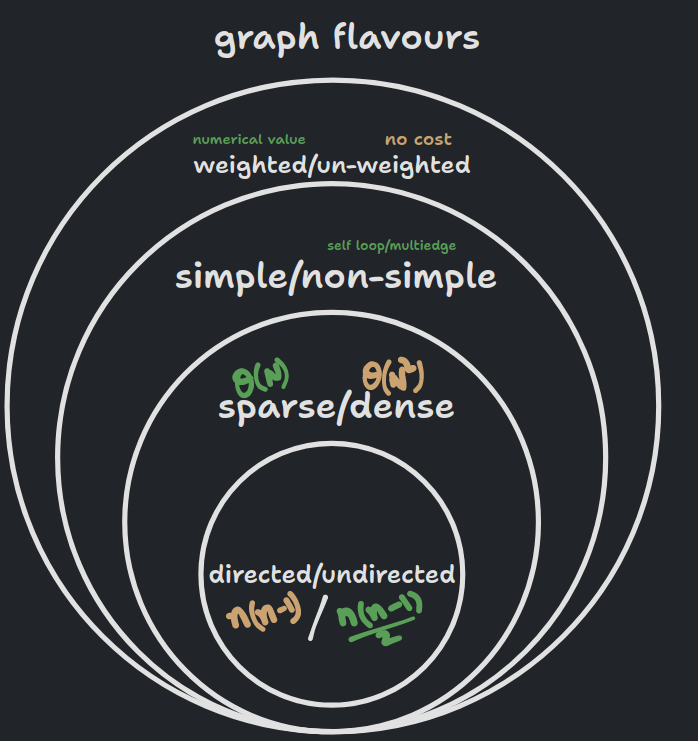
- In the diagram,
Cycle
Cyclic
Paththat starts and ends in the samevertex. AllCyclesarePath, but not opposite.- A graph can have multiple cycles
- When you start at Node(x), follow the links, and end back at Node(x)
- Needs 3 nodes
- Odd/Even cycles
odd:oddno ofverticesin the cycleeven:evenno ofverticesin the cycle
Acyclic
A graph that contains no cycles
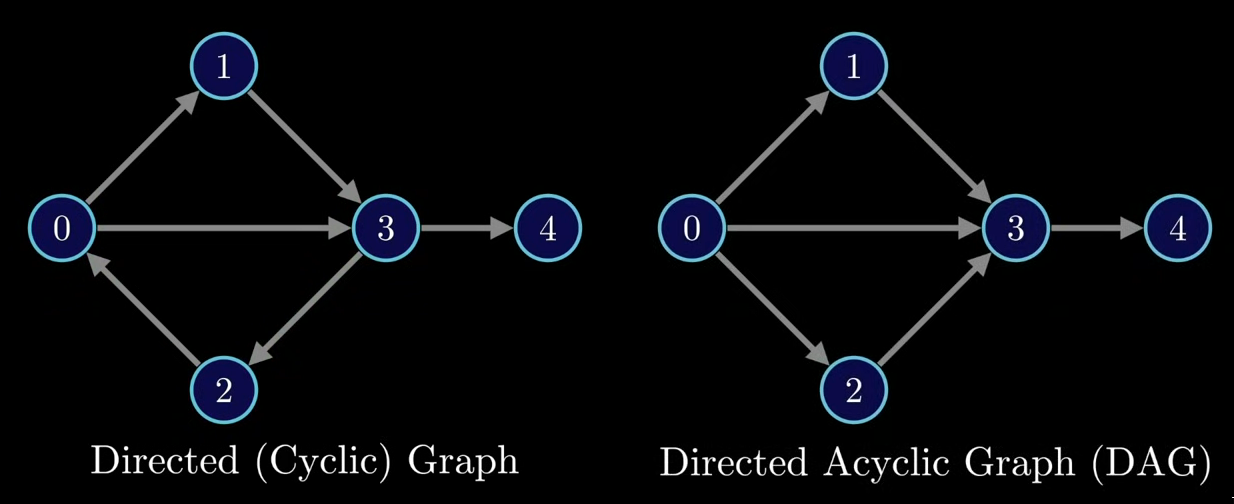
DAG
Directed, acyclic graph.
Partite
k-partite
- A graph whose vertices are (or can be) partitioned into k different independent sets.
- Recognition of
2-partite (bipartite)
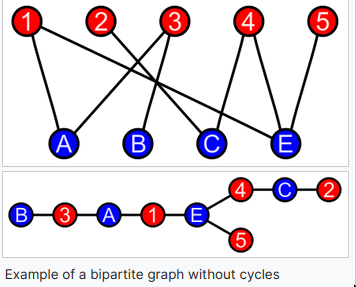
- aka
2-colorable - If there exists and partition of the vertex set into two
disjoint-sets- i.e
- If they’re adjacent then one of them is in
- i.e
- Bipartite graphs may be recognized in polynomial time
- Bipartite graphs cannot have any
odd cycles. i.eodd cyclesnot allowed.- Eg. triangle has 3
vertices, and is acycle. So triangle is not bipartite.
- Eg. triangle has 3
- How to Tell if Graph is Bipartite (by hand)
-
Types
Complete: Every vertex in one set is connected to every vertex in the other set.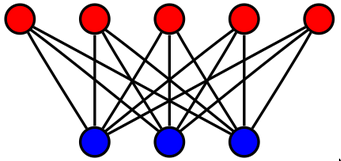
Matching: Each vertex is connected to at most one other vertex from the opposite set.Planar: Can be embedded in the plane without any edges crossing.
-
Links and resources
Others
Regular: Every vertex has the same degree.Multigraph: Allows multiple edges between the same pair of vertices.- Eg. Being able to swim across a river or take a raft across the same river is an example in games.
Graph representation
Adjacency Matrix
- Space complexity is
- Has entry for no-edges
- Has double entry for undirected edges
Adjacency List
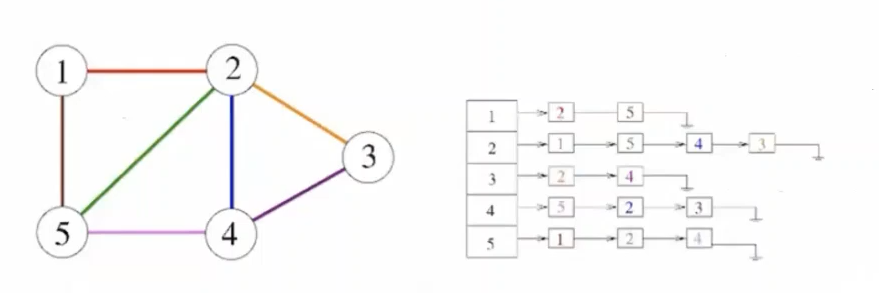
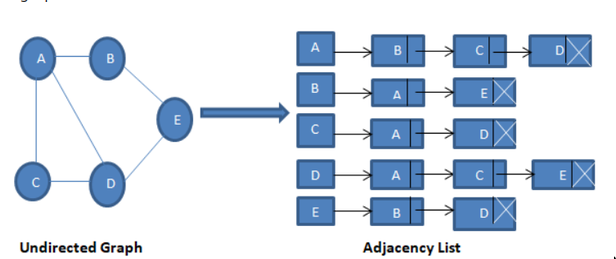
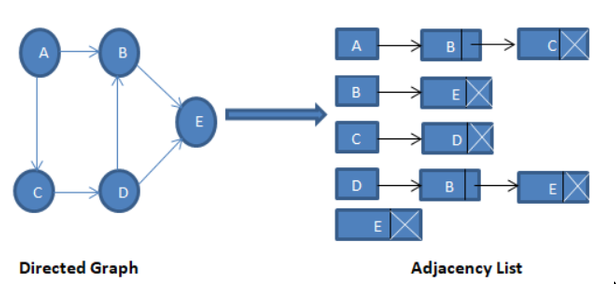
Nx1array of pointers- Each element(vertex(
- The direction/order of items in the “edge list” for each “vertex” do not tell anything about if there any network exists between a edge items themselves.
- i.e
A: [B, C], this meansAis connected toBandCbut tells us nothing about the relation ofBandC. This can be confusing becauseBandCare next to each other in a link list. In other words, link list is just the implementation and not the logical view.
- i.e
- List contains list of “what am i adjacent to”
- Each vertex (
N) has set of edges (M). No of edges per vertex is called thedegree- So, in a way no. of
neighborsof somevertexis thedegree
- So, in a way no. of
- Space complexity
- Sparse
- Space Complexity
- total
Nvertices (items in array) - total
Medges - In undirected, each connected
Nhas the edge mentioned both ways. So2M
- Space Complexity
- Dense
- Space Complexity:
- Space Complexity:
- Sparse
Graph Nodes
- Graph Nodes etc. like we do with linked list
- But we don’t do it this way in practice generally